TOPICS COVERED :
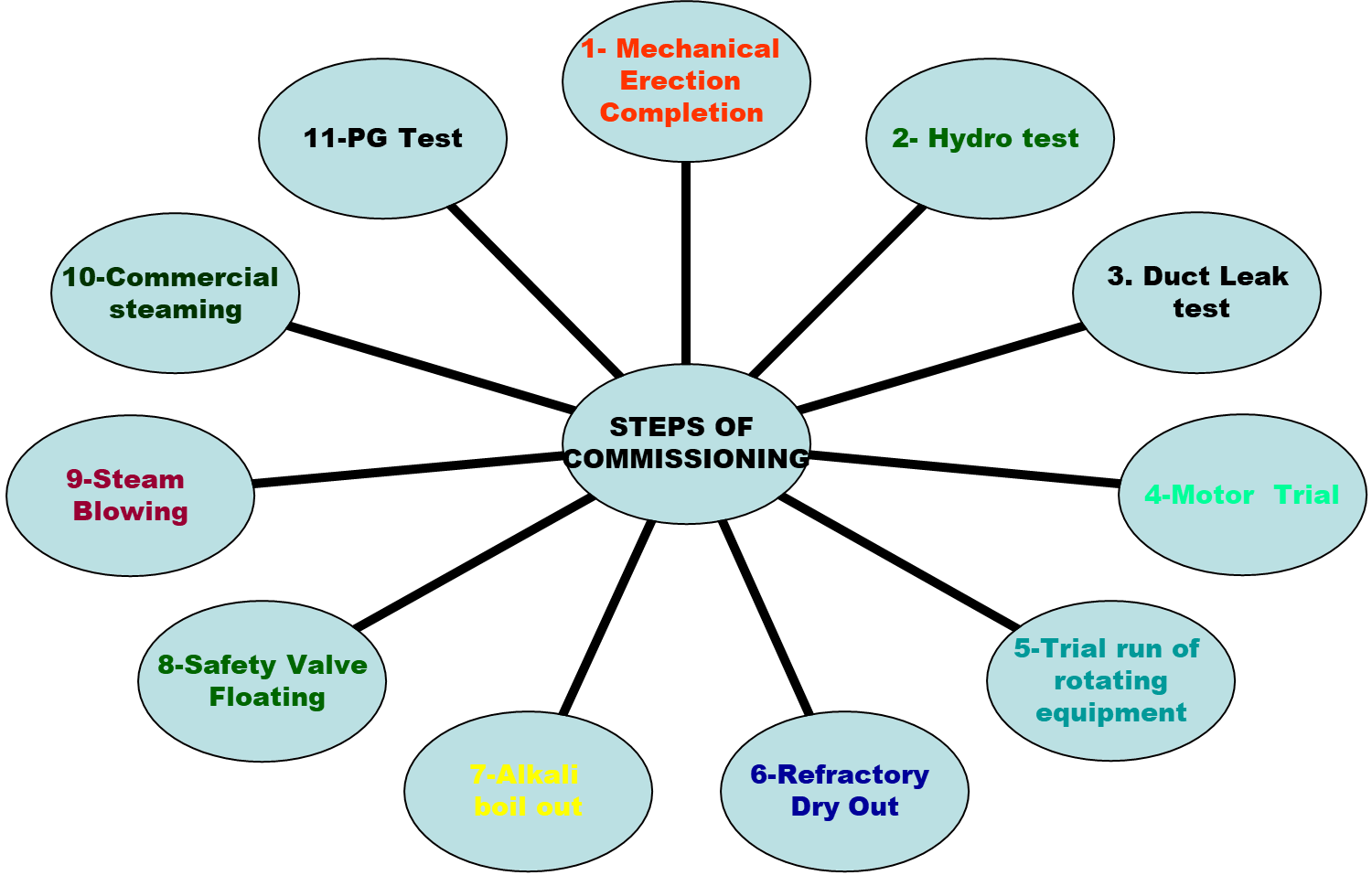
Stages of commissioning
- Pre-start checks
- Efficiency calculation
- Tips on efficient operation
- Emergencies & troubleshooting
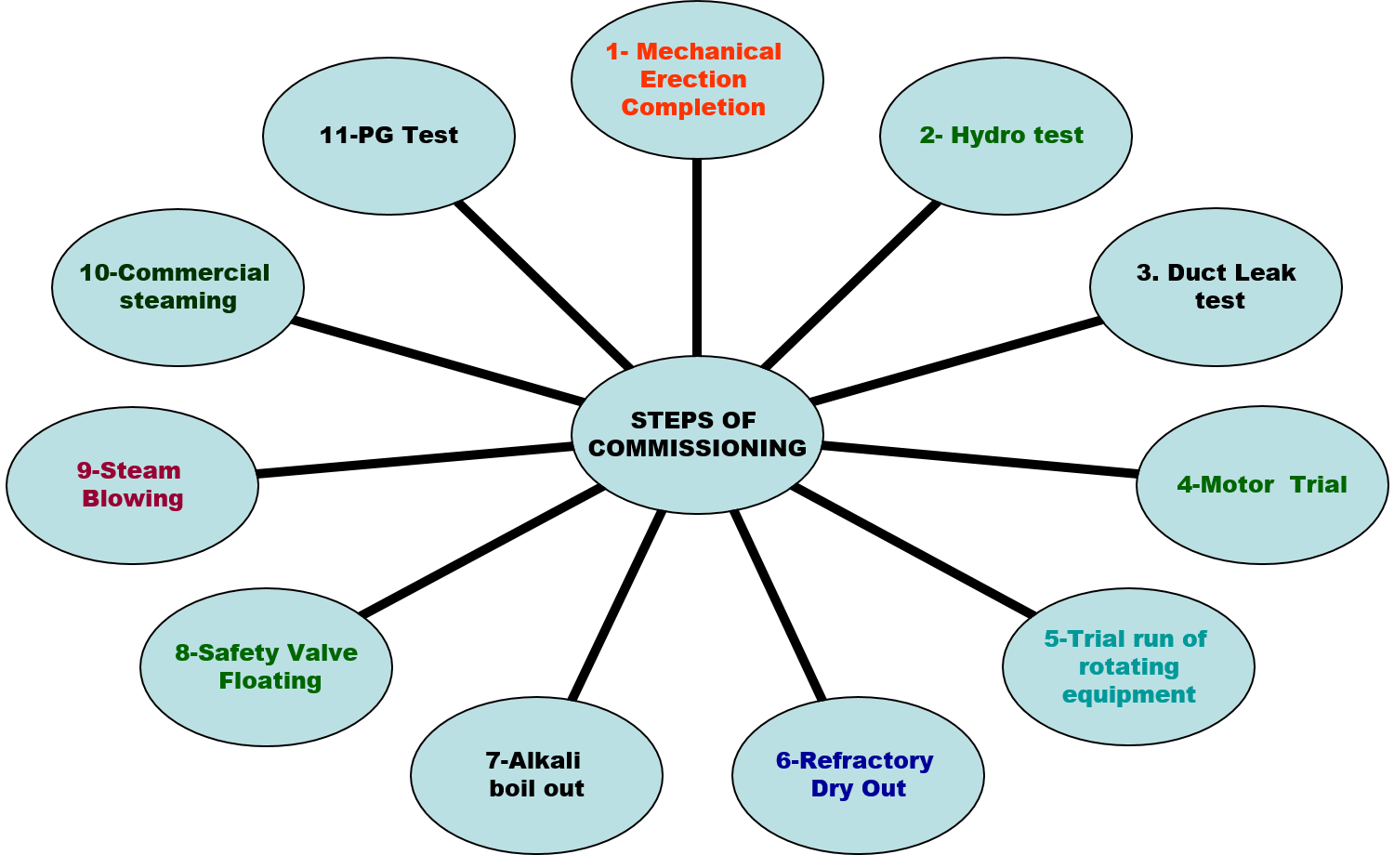
COMMISSIONING STAGES
WHY ??
To check the strength of all welding carried out and parts strength.
CARE TO BE TAKEN
•
The boiler should be in cold condition.
• Water used must be as near as possible to the boiler pressure parts temperature & the difference should not be more than 50 deg.
• Maintain boiler water pH between 8.5 to 10.5 & hydrazine to approximately 150 ppm.
• Boiler must be hydro tested to 1.5 Times design pressure only for the first time after completion of the erection as per Regulation requirement.
To ensure no Flue gas or Air leakage. This also reflects the completion of welding done on non pressure parts
IF NOT DONE:
Leakages during operation, loss in efficiency, a Load restriction
CARE TO BE TAKEN
•Take leak test of all ducting preferably with smoke.
• Take enough care for Air pre-heater Leak test
• Roof sealing to be carefully examined.
• Mark the leak area for attending it later.
• Repair with good engineering practice
WHY
Controlled & Slow heating of refractory to remove moisture within it. Pressure parts are also heated up for the first time in a controlled manner
IF NOT DONE:
Cracking or separation of refractory may occur. Pressure parts may face thermal shocks
CARE TO BE TAKEN
In deciding initial heating temperature and its duration the following factors should be considered:
•Estimated moisture content of walls and refractory.
•Thickness of walls and refractory.
•The distance from the heat source.
•Strict follow-up of Drying curve
To descale and remove foreign materials from steam pipes leading to the turbine
IF NOT DONE THEN:
Damage to turbine blades from such material in the course of normal operation.
PRINCIPLE
STEAM BLOWING IS CARRIED OUT BY THE PUFFING METHOD TO:
• Dislodge rust/scales from pipe work by thermal shocks.
• High momentum of expanding steam in the pipe work purges out the loosened material.
• It is required to create a higher momentum during steam blowing than possible during the operation of the unit. This applies to all steam piping leading to the turbine.
• Care to be taken to terminate the discharge to a safer place
• Steam blowing completion criteria to be discussed & decided as per the application of steam
you can also check power plant commissioning
PRE-START CHECK
1.. Filling the boiler
- If hot water has been used in the boiler, care should be exercised to feed slowly to avoid severe temperature strains.
- Make sure that all drains are closed before filling the boiler and that the unit is adequately vented during the filling procedure.
- Fill until water is visible in the gauge glass. The steam drum vent should remain open during the filing operation and initial firing.
- It shall not be closed until all the air is vented from the unit and an appreciable quantity of steam is issuing, therefore.
- The unit may be considered free of air when the drum pressure reaches 2 kg per cm sq.
2.. Super heater Drains/ Vents
•The superheater should be drained before lighting off through lines free from back pressure.
•The superheater drain should be closed, and the superheater outlet vent must remain open to assure a flow of steam to protect the super-heater elements from overheating until the boiler has gone on the line and is carrying the load.
•The vent valve may be throttled somewhat when the boiler pressure becomes sufficient to assure considerable flow through the superheater.
3.. Steam Gauge
The steam pressure gauges should be checked as soon as sufficient pressure is available. Blow out the connecting piping then check the action of the gauge needle to be sure that it is functioning.
4.. Water Gauge
Check & Flush the water gauge if reqd
5.. Water Level
•Water level is to be maintained at 50% level of the gauge glass.
•During normal operation, the water level in the gauge glass should be observed periodically even though the boiler is equipped with a reliable feed water regulator or remote water level indicator.
•Never shut off the feed water supply to a steaming boiler completely, not even for only a short period.
6.. Warming up Steam Lines
While the boiler is being brought up to pressure, provision should be made for gradually heating and adequately draining all cold steam piping. If the main steam line is cold, it is generally advisable to raise pressure on the line from the beginning by opening all valves.
7.. Gas Temperature
The stack gas temperature will rise with an increasing load and fall with a decreasing load. If the gas temperature is above normal, look for
a. High excess air.
b. Fouled Firesides
c. Secondary combustion
8.. Steam Temperature
The steam temperature varies with the load, raising as the load decreases.
With constant load, abnormally high superheat steam temperature may be caused by :
a. Too high excess air.
b. Too low feed water temperature
c. Secondary Combustion
d. Improper operation of automatic steam temperature indicating and control equipment.
Superheater steam temperature below normal for the load may be caused by
a. Too low excess air
b. Too high feed water temperature
c. Excessive moisture carries over from the boiler
d.Excessive external deposits on superheater tubes
e.Improper operation of automatic steam temperature
indicating and controlling equipment
9.. Blow Downs
The data on blowdowns should be recorded. Their frequency and duration are best determined from a chemical analysis of the boiler water.
•The use of the boiler bottom blow-off valves should be restricted to periods of moderate steaming rates and preferably a very low combustion rate.
•The bottom blow down should always be used to free a boiler of sediment when the boiler is being cut out.
•Never make the blow down long enough to lose sight of the water in the gauge glass.
•Check the valves for leaks occasionally
A continuous blowdown line offers the best means for controlling the concentration of soluble salts in the boiler water, because, it maintains a relatively constant concentration
10.. Soot Blowers
The soot blower should be operated as often as necessary, to keep the external heating surfaces clean. Watching the gas temperature on the stack may indicate the need for blowing soot.
Never use soot blowers on a cold boiler.
It is good practice to blow soot just before taking the boiler out of service.
Be sure that the combustion rate is high enough when blowing soot so that the fires are not extinguished.
Open the drain valve and let the steam blow freely long enough to heat the lines thoroughly before operating the soot blowers.
The soot blower piping should be drained before each use to prevent damage to the soot blower elements by slugs of water.
TIPS FOR EFFICIENT OPERATION OF BOILER
FACTORS AFFECTING PERFORMANCE OF BOILER
- Gas temperature leaving air heater
- Excess air / O2 at Eco. outlet
- Unburnt carbon in ash
- Air leakage into furnace
- Feed water and Boiler water quality
- Deaerator in service